In this section, we will be learning about the Process Synchronization and critical Section. Let us begin with an overview of the topics to be covered in this section.
- What is Process Synchronization?
- What is the Independent and cooperative Process?
- How process synchronization problem arises?
- What is the Critical Section? And what are the solutions to solve the critical section problem?
Process Synchronization
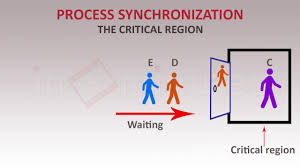
Process synchronization means sharing the system resources by the processes in such a manner that processes who access the system resources at the same time are handled, so that the chance of inconsistent data is reduced.
On the basis of synchronization, processes can be further divided into two categories
- Independent process: when one process is executing, the other processes are not being affected.
- Cooperative process: when one process is executing, the other processes may get affected.
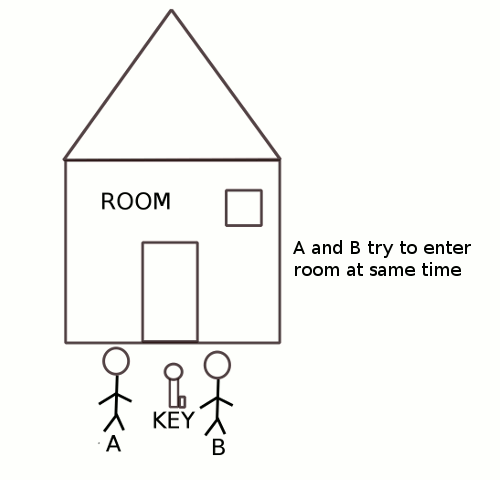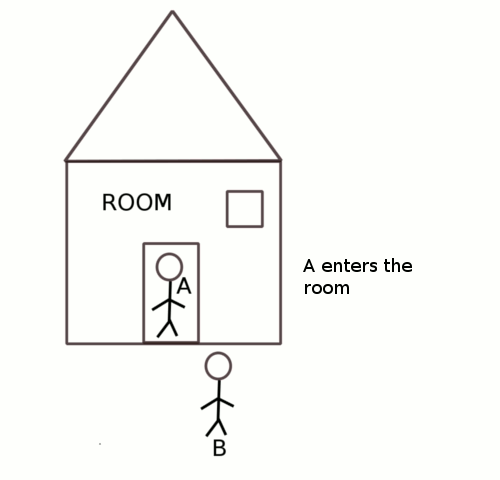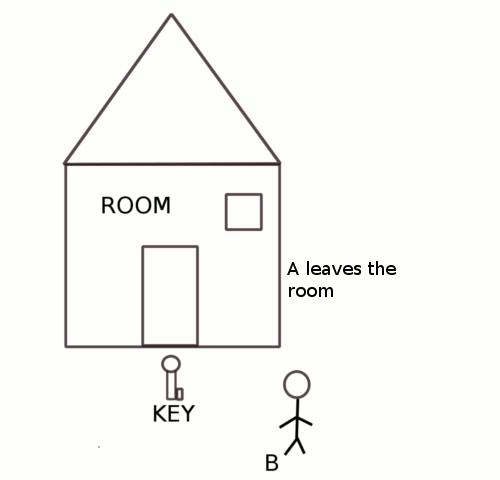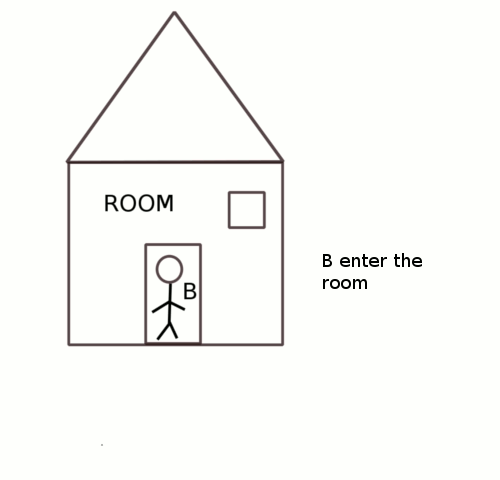
In the case of cooperative processes, there are shared resources that cause the Process synchronization problem.
When more than one process access the shared resources like memory, variables, etc. in this situation, there is a possibility that the output is wrong or the value of the shared variable is inconsistent.
As more than two processes access and manipulate the same data simultaneously, after that the output is controlled on the order in which process takes the access of the shared resources.
Critical Section
Critical Section is a code segment that gains access to variables which is used in common by other process and has to carry out instruction as an atomic action. It means that in a set of cooperating processes, at a certain point of time, only one process must be carrying out an instruction in its critical section.
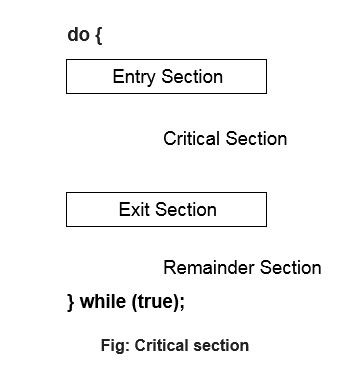
Three conditions are required to be fulfilled to solve the critical section problem:
- Bounded Waiting: a limit must exist on the amount of time other processes are permitted to get into in its critical section after any process has made a call to go in its critical section and before that call is allowed.
- Mutual Exclusion: If one process is executing inside the critical section, then any other processes must not enter the critical section.
- Progress: If no process is in its critical section and if one or more processes want to Enter in their critical section, then only those processes that are not in their remainder section can participate in the decision on which process enters their critical section next.